Quill's Quiz - 1100 Question US Mega Geography Quiz
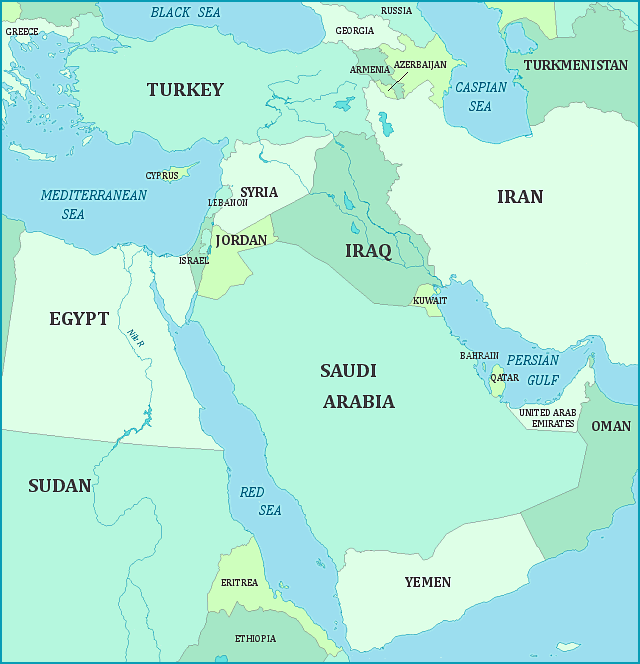
Print this map of the Middle East US States and Capitals Map Quiz
Free Maps, Map Puzzles and Educational Software: Owl and Mouse Educational Software
Print this map of the Middle East US States and Capitals Map Quiz
Free Maps, Map Puzzles and Educational Software: Owl and Mouse Educational Software
East of what and the middle of where? As with
most geographic terms it is Eurocentric — the Middle East is east as it
is to the east of Europe although it is mostly the western part of Asia.
Originally the Ottoman Empire (centered in what is now Turkey and
extending into Europe and what is now the Middle East) was referred to
as the Near East. Asia facing the Pacific was the Far East and
what was in between, from Mesopotamia (now Iraq) to Burma was the Middle
East.
In the later 1800s the “Middle East Question” was a major international concern. The question was how could Britain stop Russia from expanding south and gaining a warm water port on the Indian Ocean. With this access Russia could then take over India from Britain and become powerful enough to threaten Europe. The main focus was the Persian Gulf. Newspaper reporting on this issue popularized the term Middle East.
After World War I the Ottoman Empire dissolved and the term Near East lost currency. During World War II the fighting in the Eastern Mediterranean area was referred to by the term Middle East as it was part of the British Middle Eastern command area. By the end of the war the term had stuck. Most of the former Middle East is now South Asia and Southeast Asia, more reasonable geographical terms.
Middle East now commonly refers to the area from Syria to Yemen; Egypt to Iran. Formerly it was used for a more extensive area — Turkey to Ethiopia; Libya to Pakistan. The international airline organization, IATA, defines the Middle East as: Bahrain, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, the Palestinian territories, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Basically the Middle East is Egypt and the other Arab countries to its east plus Israel and Iran.
The term Near East has survived in Archaeology and the study of ancient history as they were unconcerned with recent developments. Today there may be programs of Near Eastern Studies and Middle Eastern Studies at the same university, studying the same region, just several thousand years apart in time.
In the later 1800s the “Middle East Question” was a major international concern. The question was how could Britain stop Russia from expanding south and gaining a warm water port on the Indian Ocean. With this access Russia could then take over India from Britain and become powerful enough to threaten Europe. The main focus was the Persian Gulf. Newspaper reporting on this issue popularized the term Middle East.
After World War I the Ottoman Empire dissolved and the term Near East lost currency. During World War II the fighting in the Eastern Mediterranean area was referred to by the term Middle East as it was part of the British Middle Eastern command area. By the end of the war the term had stuck. Most of the former Middle East is now South Asia and Southeast Asia, more reasonable geographical terms.
Middle East now commonly refers to the area from Syria to Yemen; Egypt to Iran. Formerly it was used for a more extensive area — Turkey to Ethiopia; Libya to Pakistan. The international airline organization, IATA, defines the Middle East as: Bahrain, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, the Palestinian territories, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Basically the Middle East is Egypt and the other Arab countries to its east plus Israel and Iran.
The term Near East has survived in Archaeology and the study of ancient history as they were unconcerned with recent developments. Today there may be programs of Near Eastern Studies and Middle Eastern Studies at the same university, studying the same region, just several thousand years apart in time.