Quill's Quiz - 1100 Question US Mega Geography Quiz
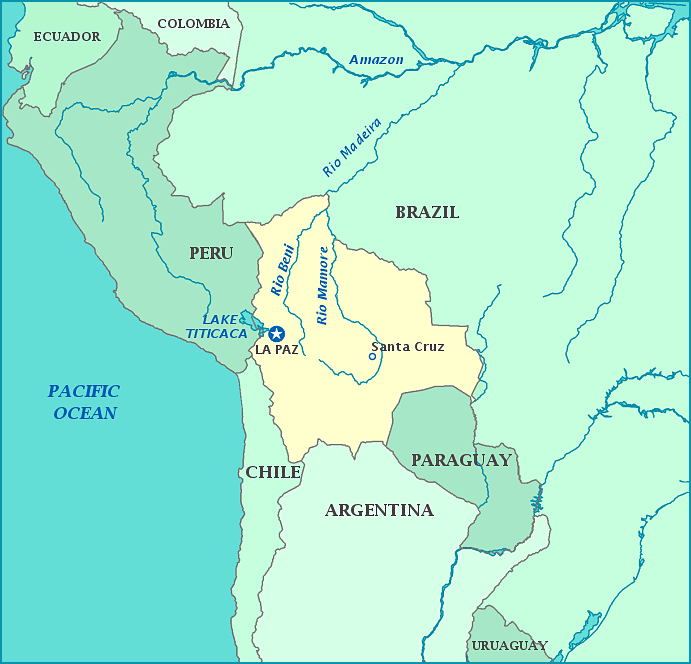
Print this map of Bolivia US States and Capitals Map Quiz
Free Maps, Map Puzzles and Educational Software: Owl and Mouse Educational Software
Print this map of Bolivia US States and Capitals Map Quiz
Free Maps, Map Puzzles and Educational Software: Owl and Mouse Educational Software
Officially called the Plurinational State of Bolivia, the region was inhabited by the Inca, who ruled from 1438 until 1527, when the Spanish arrived. The Spanish quickly conquered the area and settled it in the following years, claiming it as the Viceroyalty de la Rio de La Plata.
Simon Bolivar, for whom the country was later named, led the revolt against Spain in 1809, taking advantage of the mother country, having been weakened severely by the Napoleonic Wars and being an ocean away. Since independence in 1835, Bolivia has seen instability and lost several peripheral territories, including Aere, Gran Chaco, and its coast.
When the Nationalist Movement Party was denied political victory in 1951, it sparked a revolt that broke out the following year. Despite the violence, the country earned universal suffrage, rural education, and improved working conditions in mines that still produced silver. 1961-1982 saw more violence, especially within politics, leading to coups, and instability. After years of self-proclaimed presidents who held office purely by force, heavy communist influence, fragmented political parties social unrest, violent interference from terrorists, and presidential drug trafficking, the country finally began to see stability and peace in 2009.
The country is a landlocked and divided into three geographic regions: Andean, sub-Andean, and the Llanos (the Amazon River). Climates vary from tropical rainforest to desert, with subtropical or even polar climates in higher altitudes. Despite the deplorable conditions they suffered thanks to the settlers' mistreatment, native people remained the majority of the population, and have influenced the culture, along with Latin peoples.
Simon Bolivar, for whom the country was later named, led the revolt against Spain in 1809, taking advantage of the mother country, having been weakened severely by the Napoleonic Wars and being an ocean away. Since independence in 1835, Bolivia has seen instability and lost several peripheral territories, including Aere, Gran Chaco, and its coast.
When the Nationalist Movement Party was denied political victory in 1951, it sparked a revolt that broke out the following year. Despite the violence, the country earned universal suffrage, rural education, and improved working conditions in mines that still produced silver. 1961-1982 saw more violence, especially within politics, leading to coups, and instability. After years of self-proclaimed presidents who held office purely by force, heavy communist influence, fragmented political parties social unrest, violent interference from terrorists, and presidential drug trafficking, the country finally began to see stability and peace in 2009.
The country is a landlocked and divided into three geographic regions: Andean, sub-Andean, and the Llanos (the Amazon River). Climates vary from tropical rainforest to desert, with subtropical or even polar climates in higher altitudes. Despite the deplorable conditions they suffered thanks to the settlers' mistreatment, native people remained the majority of the population, and have influenced the culture, along with Latin peoples.